Dr.-Ing. Florian Thamm
Please do not call me in the office. Write me an E-Mail instead 🙂
Wanna’ see how we synthesized 57 300 000 000 (!) patients out of 151?
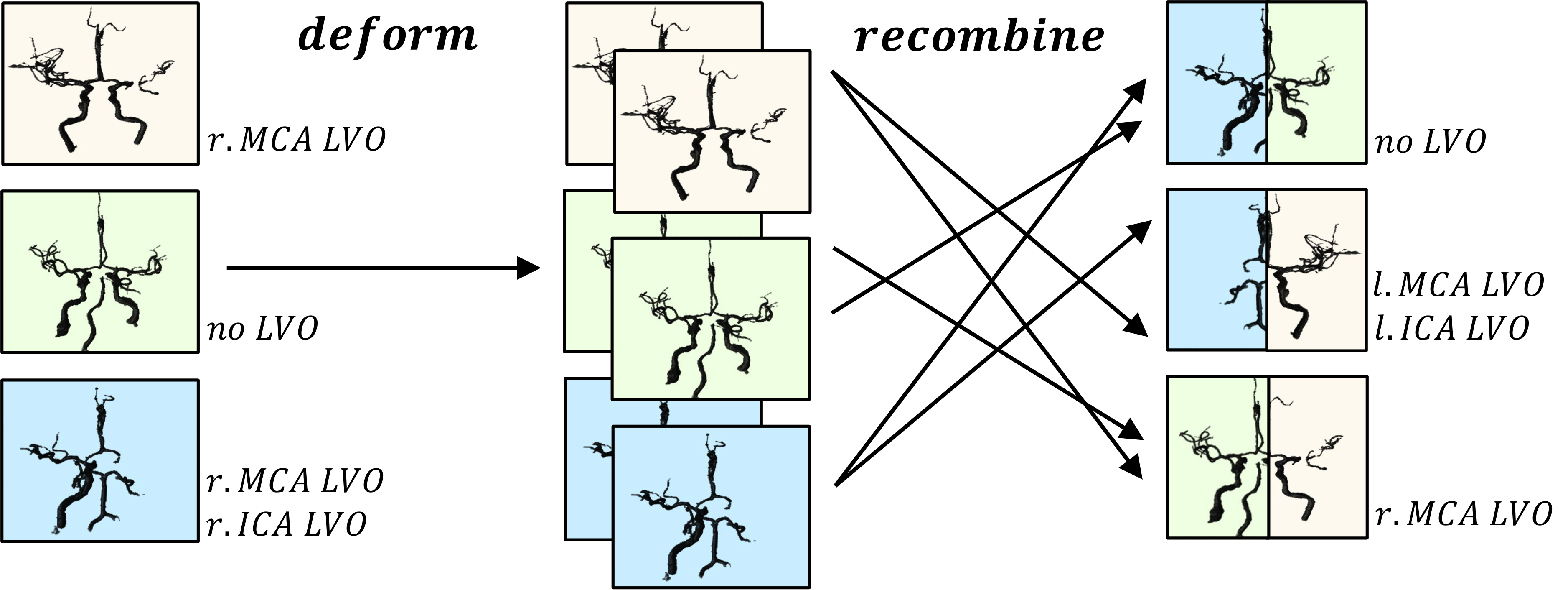
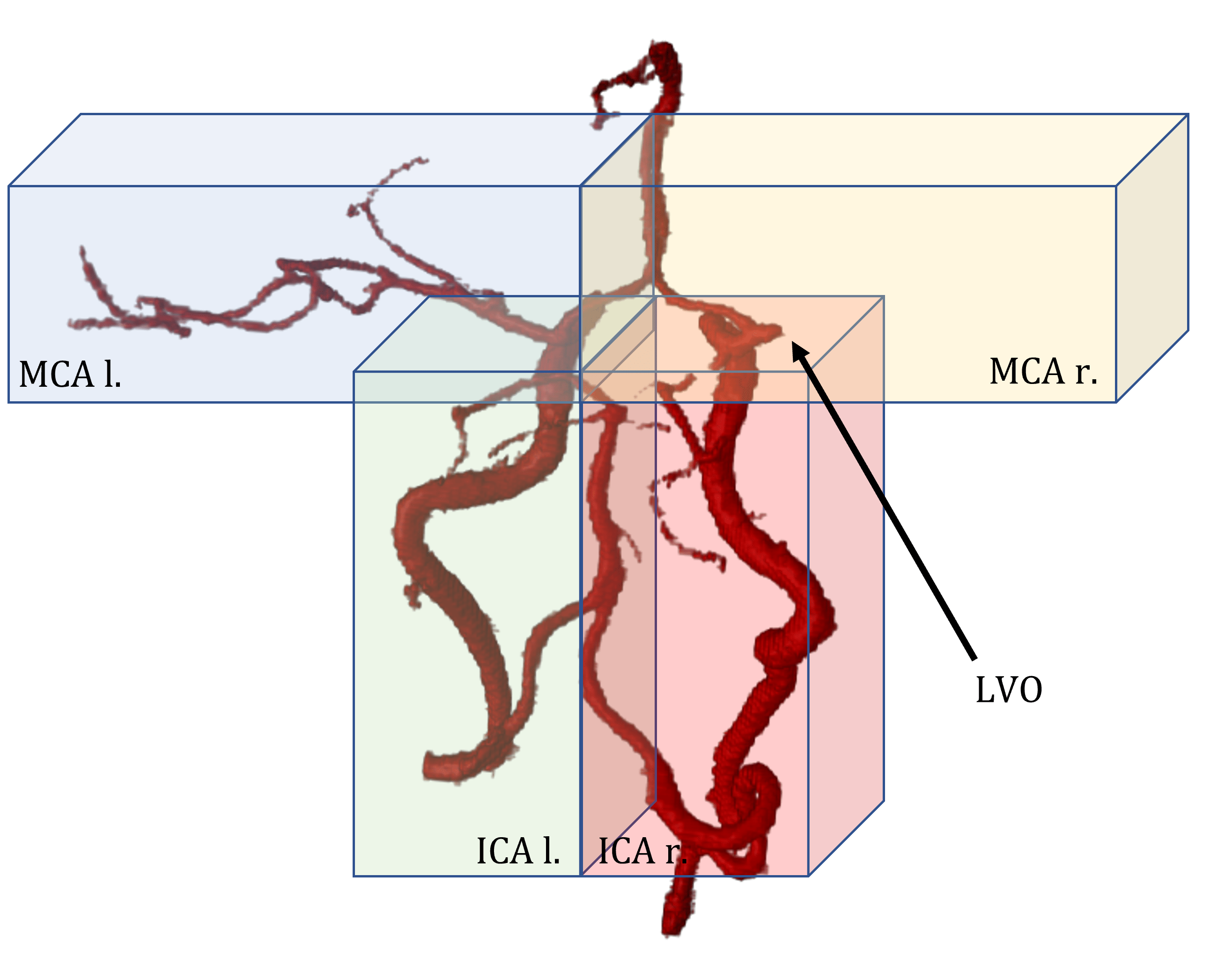
Check out our most recent work “Building Brains” [arXiv] accepted at MICCAI to see how we pushed the detection of LVOs even further! Open the Projects tab below ; )
Building Brains: Subvolume Recombination for Data Augmentation in Large Vessel Occlusion Detection
Ischemic strokes are often caused by large vessel occlusions (LVOs), which can be visualized and diagnosed with Computed Tomography Angiography scans. As time is brain, a fast, accurate and automated diagnosis of these scans is desirable. Human readers compare the left and right hemispheres in their assessment of strokes. A large training data set is required for a standard deep learning-based model to learn this strategy from data. As labeled medical data in this field is rare, other approaches need to be developed. To both include the prior knowledge of side comparison and increase the amount of training data, we propose an augmentation method that generates artificial training samples by recombining vessel tree segmentations of the hemispheres or hemisphere subregions from different patients. The subregions cover vessels commonly affected by LVOs, namely the internal carotid artery (ICA) and middle cerebral artery (MCA). In line with the augmentation scheme, we use a 3D-DenseNet fed with task-specific input, fostering a side-by-side comparison between the hemispheres. Furthermore, we propose an extension of that architecture to process the individual hemisphere subregions. All configurations predict the presence of an LVO, its side, and the affected subregion. We show the effect of recombination as an augmentation strategy in a 5-fold cross validated ablation study. We enhanced the AUC for patient-wise classification regarding the presence of an LVO of all investigated architectures. For one variant, the proposed method improved the AUC from 0.73 without augmentation to 0.89. The best configuration detects LVOs with an AUC of 0.91, LVOs in the ICA with an AUC of 0.96, and in the MCA with 0.91 while accurately predicting the affected side.
Can you tell which one is fake?
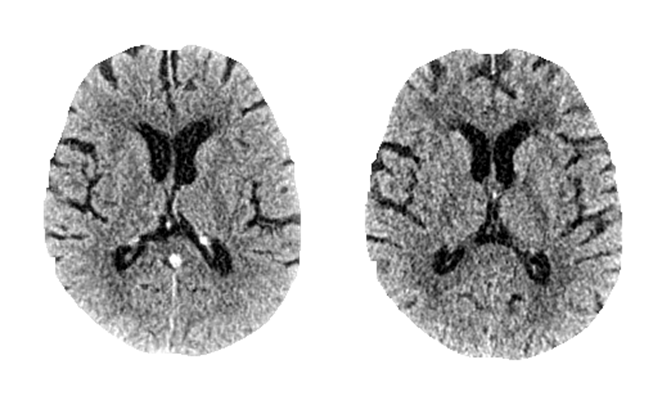
No? Don’t worry*, radiologists neither can 😉 Check out our most recent work “SyNCCT” published at MICCAI to see how we synthesized CT images from angiography scans.
SyNCCT: Synthetic Non-contrast Images of the Brain from Single-Energy Computed Tomography Angiography
By injecting contrast agent during a CT acquisition, the vascular system can be enhanced. This acquisition type is known as CT Angiography (CTA). However, due to typically lower dose levels of CTA scans compared to non-contrast CT acquisitions (NCCT) and the employed reconstruction designed specifically for vessel reconstruction, soft tissue contrast in the brain parenchyma is usually subpar. Hence, an NCCT scan is preferred for the visualization of such tissue. We propose SyNCCT, an approach which synthesizes NCCT images from the CTA domain by removing enhanced vessel structures and improving soft tissue contrast. Contrary to virtual non-contrast (VNC) images based on dual energy scans, which target the physically accurate removal of iodine rather than generating a realistic NCCT with improved gray/white matter separation, our approach only requires a conventional single-energy acquisition. By design, our method integrates prior domain knowledge and employs residual learning as well as a discriminator to achieve perceptual realism. In our data set of patients with ischemic stroke, the absolute differences in automatic ASPECT scoring, which rates early signs of an occlusion in the anterior circulation on a scale from 0 (most severe) to 10 (no signs), was 0.78 ± 0.75 (median of 1) when comparing our SyNCCT to the real NCCT images. Qualitatively, realistic appearance of the images was confirmed by means of a Turing test with a radiologist, who classified 64% of 64 (32 real, 32 generated) images correctly. Two other physicians classified 65% correctly, on average.
*And by the way, the left one was fake 😉
VirtualDSA++: Automated Segmentation, Vessel Labeling, Occlusion Detection and Graph Search on CT-Angiography Data
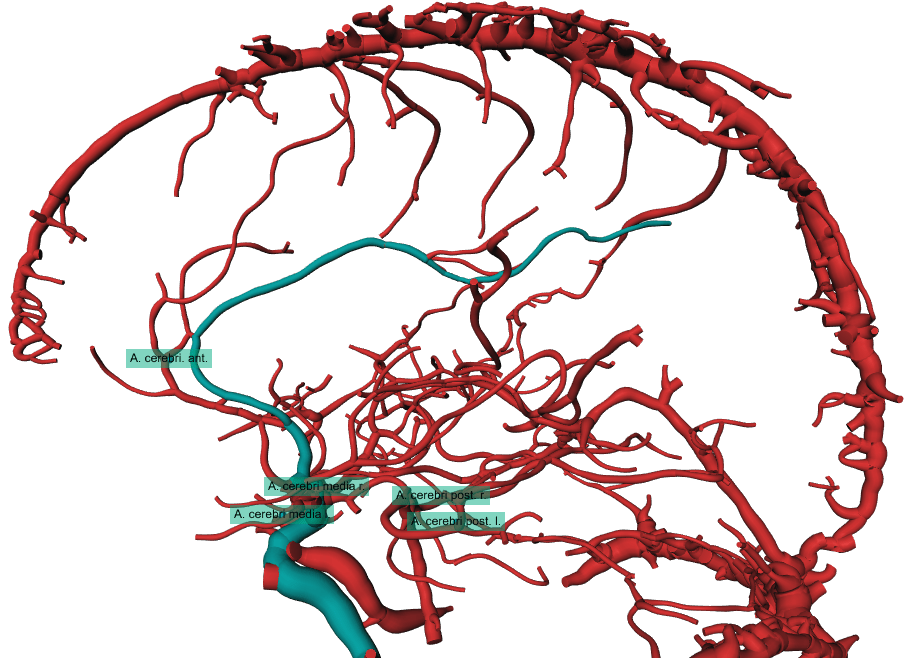
Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) is one of the most commonly used modalities in the diagnosis of cerebrovascular diseases like ischemic strokes. Usually, the anatomy of interest in ischemic stroke cases is the Circle of Willis and its peripherals, the cerebral arteries, as these vessels are the most prominent candidates for occlusions. The diagnosis of occlusions in these vessels remains challenging, not only because of the large amount of surrounding vessels but also due to the large number of anatomical variants. We propose a fully automated image processing and visualization pipeline, which provides a full segmentation and modelling of the cerebral arterial tree for CTA data. The model itself enables the interactive masking of unimportant vessel structures e.g. veins like the Sinus Sagittalis, and the interactive planning of shortest paths meant to be used to prepare further treatments like a mechanical thrombectomy. Additionally, the algorithm automatically labels the cerebral arteries (Middle Cerebral Artery left and right, Anterior Cerebral Artery, Posterior Cerebral Artery left and right) and detects occlusions or interruptions in these vessels. The proposed pipeline does not require a prior non-contrast CT scan and achieves a comparable segmentation appearance as in a Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA).
https://diglib.eg.org/bitstream/handle/10.2312/vcbm20201181/151-155.pdf
A 1minute Teaser 😉
And here is more Material
Watch the playlist with 3 videos on youtube https://youtu.be/b_IshmarO7E?list=PLJgm15h1F7z5pvrb6qHB9Z0QHbcALefQj
- 11/2019 – 10/2023
Dr.-Ing Computer Science at Pattern Recognition Lab, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg - 04/2017 – 10/2019
M.Sc. Computer Science, 1.1, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg - 10/2013 – 03/2017
B.Eng. Medical Engineering, 1.4, Technische Hochschule Nürnberg
Siemens AG, Erlangen
- since 09/2024
Senior Key Expert in Artificial Intelligence
IT DA AL PPS - 03/2024 – 09/2024
Senior Data Scientist
IT DA AL PLF - 10/2022 – 02/2024
Data Scientist
IT DA AL PLF
Siemens Healthcare GmbH, Forchheim
- 11/2019 – 09/2022
Ph.D. Candidate
CT R&D CTC SA - 03/2019 – 09/2019
Master’s Thesis Student
CT R&D CTC SA - 03/2017 – 03/2019
Working Student
CT R&D APP ALG - 10/2016 – 04/2017
Bachelor’s Thesis Student
AT R&D APP RH - 03/2016 – 10/2016
Working Student
AT R&D APP REC - 10/2015 – 03/2016
Intern
AT R&D APP REC
Friedrich-Alexander-University
- Since 01/2022
Researcher - 01/2020 – 01/2022
Research Assistant for CTA Image Analysis
Exercise Instructor of the Deep Learning Course - 10/2018 – 12/2020
Teaching Assistant, Exercise Instructor of the Deep Learning Course
Technische Hochschule Nürnberg
- 03/2015 – 10/2015
E-Learning Tutor - 10/2014 – 10/2015
Teaching Assistant
2024
- , , , , , , , , , , :
Improved detection of small pulmonary embolism on unenhanced computed tomography using an artificial intelligence-based algorithm – a single centre retrospective study
In: International Journal of Cardiovascular Imaging (2024)
ISSN: 1569-5794
DOI: 10.1007/s10554-024-03222-8
BibTeX: Download - , , , , :
Privacy-enhancing Image Sampling for the Synthesis of High-quality Anonymous Chest Radiographs
German Conference on Medical Image Computing, BVM 2024 (Erlangen, March 10, 2024 - March 12, 2024)
In: Andreas Maier, Thomas M. Deserno, Heinz Handels, Klaus Maier-Hein, Christoph Palm, Thomas Tolxdorff (ed.): Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin 2024. BVM 2024, Wiesbaden: 2024
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-658-44037-4_12
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , :
Deep learning based drill wear segmentation and analysis of the wear progress
In: International Journal on Interactive Design and Manufacturing (2024)
ISSN: 1955-2513
DOI: 10.1007/s12008-024-02045-0
BibTeX: Download
2023
- , , , :
Generation of Anonymous Chest Radiographs Using Latent Diffusion Models for Training Thoracic Abnormality Classification Systems
2023 IEEE 20th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) (Cartagena, Colombia, April 18, 2023 - April 21, 2023)
In: 2023 IEEE 20th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) 2023
DOI: 10.1109/ISBI53787.2023.10230346
BibTeX: Download - , , , , :
Deep Learning-Based Anonymization of Chest Radiographs: A Utility-Preserving Measure for Patient Privacy
International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2023 (Vancouver, October 8, 2023 - October 12, 2023)
In: Greenspan H, Madabhushi A, Mousavi P, Salcudean S, Duncan J, Syeda-Mahmood T, Taylor R (ed.): Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2023, Cham: 2023
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-031-43898-1_26
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , , , , , :
Spatial Lesion Graphs: Analyzing Liver Metastases with Geometric Deep Learning for Cancer Survival Regression
20th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, ISBI 2023 (Cartagena, April 18, 2023 - April 21, 2023)
In: Proceedings - International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging 2023
DOI: 10.1109/ISBI53787.2023.10230367
BibTeX: Download - , , , :
Cerebral Vessel Tree Estimation from Non-contrast CT using Deep Learning Methods
Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin 2023 (, June 1, 2023 - June 1, 2023)
In: Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin 2023 2023
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-658-41657-7_15
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , :
Unsupervised Deep Learning for Advanced Forming Limit Analysis in Sheet Metal: A Tensile Test-Based Approach
In: Materials 16 (2023), p. 7001
ISSN: 1996-1944
DOI: 10.3390/ma16217001
BibTeX: Download - :
Deep Learning and Image Processing for Stroke Diagnosis with Computed Tomography Angiography (Dissertation, 2023)
DOI: 10.25593/open-fau-45
URL: https://open.fau.de/handle/openfau/30091
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , :
Detection of Pulmonary Embolisms in NCCT Data Using nnDetection
Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin Workshop, BVM 2023 (Braunschweig, July 2, 2023 - July 4, 2023)
In: Thomas M. Deserno, Heinz Handels, Andreas Maier, Klaus Maier-Hein, Christoph Palm, Thomas Tolxdorff (ed.): Informatik aktuell 2023
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-658-41657-7_28
BibTeX: Download
2022
- , , , , :
Detecting Large Vessel Occlusions using Graph Deep Learning
GeoMedIA 2022 Workshop Submission
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , :
Thrombus Detection in Non-Contrast Head CT using Graph Deep Learning
Bildverarbeitung in der Medizin 2022 (Heidelberg)
In: Bildverarbeitung in der Medizin 2022
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-658-36932-3_33
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , :
Bifurcation matching for consistent cerebral vessel labeling in CTA of stroke patients
In: International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery (2022)
ISSN: 1861-6410
DOI: 10.1007/s11548-022-02750-9
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , :
An Algorithm for the Labeling and Interactive Visualization of the Cerebrovascular System of Ischemic Strokes
In: Biomedical Physics and Engineering Express (2022)
ISSN: 2057-1976
DOI: 10.1088/2057-1976/ac9415
BibTeX: Download - , , , , :
Detection of Large Vessel Occlusions using Deep Learning by Deforming Vessel Tree Segmentations
Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin 2022 (Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum, Heidelberg, Deutschland, March 20, 2022 - March 22, 2022)
In: Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin 2022 2022
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-658-36932-3_9
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , :
Building Brains: Subvolume Recombination for Data Augmentation in Large Vessel Occlusion Detection
Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention - MICCAI 2022 (Singapore, September 18, 2022 - September 22, 2022)
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-031-16437-8_61
URL: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-031-16437-8_61
BibTeX: Download
2021
- , , , , :
Failure and Risk Analysis based on Maintenance Reports of Machines Components in Manufacturing Industry
XIII. International Conference on the Theory of Machines and Mechanisms - TMM2020 (Liberec, September 7, 2021 - September 9, 2021)
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-83594-1_29
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , :
Segmentation of the Carotid Lumen and Vessel Wall using Deep Learning and Location Priors
(2021)
BibTeX: Download
(Conference report) - , , , :
Abstract: VirtualDSA++: Automated Segmentation, Vessel Labeling, Occlusion Detection and Graph Search on CT-Angiography Data
BVM Workshop 2021 (OTH Regensburg, March 8, 2021 - March 9, 2021)
In: BVM Workshop 2021
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , :
SyNCCT: Synthetic Non-Contrast Images of the Brain from Single-Energy Computed Tomography Angiography
Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2021 (Strasbourg, September 27, 2021 - October 1, 2021)
In: Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2021, Cham: 2021
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-87234-2_64
URL: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-87234-2_64
BibTeX: Download
2020
- , , , , , , , :
RinQ Fingerprinting: Recurrence-Informed Quantile Networks for Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting
Bilderverarbeitung für die Medizin Algorithmen - Systeme - Anwendungen (Berlin, March 15, 2020 - March 17, 2020)
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-32248-9_11
BibTeX: Download - , , , :
VirtualDSA++: Automated Segmentation, Vessel Labeling, Occlusion Detection and Graph Search on CT-Angiography Data
Eurographics Workshop on Visual Computing for Biology and Medicine (Uni Tübingen, September 28, 2020 - October 1, 2020)
In: K. Nieselt and R. G. Raidou (ed.): Eurographics Workshop on Visual Computing for Biology and Medicine 2020
DOI: 10.2312/vcbm.20201181
BibTeX: Download
2019
- , , , , , , , , :
Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting Reconstruction Using Recurrent Neural Networks
In: Rainer Röhrig, Harald Binder, Hans-Ulrich Prokosch, Ulrich Sax, Irene Schmidtmann, Susanne Stolpe, Antonia Zapf (ed.): German Medical Data Sciences: Shaping Change – Creative Solutions for Innovative Medicine, IOS Press, 2019, p. 126-133 (Studies in Health Technology and Informatics, Vol.267)
DOI: 10.3233/SHTI190816
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , , :
RinQ Fingerprinting: Recurrence-Informed Quantile Networks for Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting
Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (Shenzhen, October 13, 2019 - October 17, 2019)
In: Proceedings of MICCAI 2019, Cham: 2019
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-32248-9_11
BibTeX: Download